This week’s inspirational quote tells a hard truth. The photo below is from Geeamana, Romania,…
The post Earth911 Inspiration: Strange Days appeared first on Earth911.

This week’s inspirational quote tells a hard truth. The photo below is from Geeamana, Romania,…
The post Earth911 Inspiration: Strange Days appeared first on Earth911.
Last week, the leaders of the world’s seven biggest economies convened in Italy to discuss several pressing global issues during the annual gathering known as the G7 summit. They agreed to lend Russia’s frozen assets to Ukraine, pushed for a ceasefire in Gaza, and pledged to launch a migration coalition.
Those discussions, which concluded Saturday, came right on the heels of the annual Bonn Climate Change Conference, which sets the foundation for the United Nations’ yearly climate gathering. In Bonn, Germany, an enduring dispute over who should provide trillions of dollars in climate aid to poor nations once again ended with little progress toward a solution, dominating the agenda so much so that dialogues on other issues often reverted back to financial debates.
Government heads at both conferences barely addressed what may be one of the most pressing questions the world faces: how to respond to the immense role animal agriculture plays in driving climate change. This continues a pattern of evasion around this issue on the international stage, which advocates and scientists find increasingly frustrating, given that shrinking the emissions footprint of global livestock production and consumption is a needed step toward mitigating climate change.
“We’re seeing, essentially, the cow in the room being ignored,” said Stephanie Feldstein, population and sustainability director at the Center for Biological Diversity. “We’re seeing these kinds of vague references to needing to shift diets, but still a refusal to call out animal agriculture as the leading cause, by far, of agricultural emissions, as well as other forms of environmental destruction in food and agriculture systems.”
Although estimates vary, peer-reviewed studies have found that the global food system is responsible for roughly one-third of human-caused greenhouse gas emissions. Animals raised for consumption generate 32 percent of the world’s methane emissions, and agriculture is the largest source of anthropogenic methane pollution. Methane is the second most abundant greenhouse gas after carbon, and it’s 80 to 90 percent more powerful than carbon in its first 20 years in the atmosphere. This is why many scientists believe that aggressively curbing humanity’s methane pollution would be the fastest way to slow planetary warming. And methane isn’t the only environmental problem associated with meat and dairy. Even though animal agriculture provides 17 percent of the world’s calories, it accounts for 80 percent of global agricultural land use and 41 percent of global agricultural water use, which translates into an outsize impact on biodiversity.
Despite the mountain of evidence establishing a connection between the food we eat and climate change, the subject has only recently begun to pop up at international conferences. The big breakthrough came at last December’s U.N. climate conference, COP28, where more than two-thirds of countries in attendance, including the U.S. and the European Union, pledged to take steps to reduce the colossal climate footprint of food systems. Around the same time, the U.N. Food and Agricultural Organization, or FAO, unveiled its first-ever installment of a roadmap for transforming the global food system to limit warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius (2.7 degrees Fahrenheit).
However, the FAO roadmap came under criticism because its slate of proposed solutions almost entirely omitted the need to reduce human consumption of meat and dairy. Some researchers later asked the FAO to retract its report, alleging that it misrepresented their work by minimizing reduced meat intake as a way to cut agricultural emissions.
The failure of delegates at COP28 to directly address the causal relationship between meat consumption and climate change was just repeated by G7 nations and the Bonn climate conference attendees. These failures show how “incredibly politically charged” this issue is in multinational gatherings dominated by countries with very high rates of meat and dairy consumption, said Martin Frick, who heads up the World Food Programme’s Berlin office.
“We are moving in the right direction, but we are not moving fast enough,” said Frick. “Unless we are really serious about food, and look at it from a systems approach, ask ourselves the hard questions and give ourselves the hard answers, I don’t see how we can fix climate change.”
Still, some do see progress.
“Only six months ago, 159 governments at world-leader level made a commitment to incorporate food into their climate plans,” said Edward Davey, senior advisor of the Food and Land Use Coalition based at the World Resources Institute. The COP28 pledge includes incorporating the climate footprint of food into each country’s “nationally determined contribution,” or NDC — a specific emissions target required by the Paris Agreement.
Countries are expected to submit new NDCs by next February, and Davey said those updates will indicate whether those countries are taking the pledge seriously.
Until then, how the topic surfaces in international gatherings is the next best benchmark. “I wanted to see that food was genuinely getting its moment in the sun in the climate talks,” said Davey. “And I think what we saw was that the Bonn talks were largely focused on finance, and less on particular sectors.”
Food was not entirely absent from the G7 summit agenda. At the gathering in southern Italy, Italian prime minister Giorgia Meloni announced the launch of the Apulia Food Systems Initiative, a climate and food policy aimed at investing in resilient food systems for poorer countries. It commits an undisclosed amount of funding to strengthen agricultural climate adaptation, with most aid allocated across the African continent, where climate change is intensifying food insecurity. The initiative will back a U.S. State Department-led crop research effort, a project to create more resilient coffee supply chains, and technical support for implementing the COP28 food and agriculture pledge into countries’ NDCs.
Unsurprisingly, it does not include any projects to decarbonize animal agriculture. “Livestock is clearly a very good example of what wasn’t tackled directly, in the sense that there is no mention of livestock, per se,” said Francesco Rampa, head of the think tank European Centre for Development Policy Management’s sustainable food systems team, who assisted the Italian G7 presidency in developing the initiative. Rampa is quick to add that this is because the Apulia plan is structured to help poor nations that have negligible emissions from animal agriculture, and not higher-income countries with sizable contributions — like the G7 countries themselves.
Past G7 food initiatives have faced criticism for limited clarity and accountability around finance pledges, for not reaching small farmers, and for failing to facilitate a transition to more sustainable and equitable food systems in the places they aim to aid. Multiple experts told Grist they don’t expect the new Apulia pledge to buck that trend.
“I’m skeptical of the ability of the international community to act in a way, with the urgency, that this whole issue requires,” said William Dietz, director of research and policy at the Global Food Institute at George Washington University. “We’ve got a generation of leaders like Nero who are fiddling while the world is burning.”
This story was originally published by Grist with the headline Food’s climate footprint was once again MIA at global talks on Jun 21, 2024.
Kathrin Zangerl is a pediatrician at the Heidelberg Institute of Global Health in Germany, where she is a specialist on how climate change affects children at different stages in their lives. For instance, an infant’s developing lungs make her more susceptible to lasting harm from air pollution. A teenager, on the other hand, might be more likely to become part of the mental health pandemic among adolescents, where climate anxiety is a factor.
In other words, children have differing needs, more vulnerability, and interventions that work for adults might not work for kids.
“Children are not tiny adults,” she said.
So when Zangerl and other researchers combed through the official national climate adaptation plans of 160 countries, they were looking for consideration of the needs and roles of children, especially when it comes to health. How many countries are taking kids into account when they think about climate change?
In an article published earlier this month in The Lancet, Zangerl and her team revealed their findings: Not many.
It’s not that national climate adaptation plans have the force of law, but they can guide policymakers and attract focused funding from richer countries to low and middle-income countries. International bodies, like the United Nations, its Framework Convention on Climate Change, UNFCCC, the World Health Organization, and UNICEF, are increasingly urging countries to consider the specific needs of children in their climate policies.
The numbers were dismaying.
Nearly a third of the plans — 28 percent —did not mention children at all. Another third — 31 percent — mentioned children in only one area, such as education. And none mentioned children’s mental health.
As Zangerl wrote in the article: “Children’s mental health is a crucial public health concern that requires immediate action.”
Sudan, one of the poorest countries in the world, scored the highest in the report for its number of mentions of children in its plan. But Zangerl said that’s grading on a curve.
“No country comprehensively addressed child health needs,” she said. “A few countries were better than others, but they weren’t really good.”
“I’m not surprised,” said Tooba Akhtar, a PhD researcher at Trinity College Dublin, who was not involved in this study. She focuses on the development and well-being of children affected by climate change.
Akhtar and two of her colleagues, Kristin Hadfield and Alina Paula Cosma, wrote a recent open letter to the U.N. Climate Change Secretariat. They looked for evidence supporting programs that would help young children cope with the emotional toll of climate disasters, and found none.
“Our hunch is that these programs do not actually exist,” Akhtar said.
This is personal for Akhtar, who grew up in Pakistan. She was recently speaking to a friend working for a nonprofit there, documenting the aftermath of the devastating 2022 floods. Camps for displaced survivors have set up makeshift schools.
“Who’s attending? Children who are already school-aged. Those under 6 are forgotten.” Akhtar said that simple programs for very young children, like shared book reading, could promote social-emotional skills and parent-child bonding, helping entire families cope with post-traumatic stress. But that’s rarely happening. “The father’s off managing the land that’s been destroyed, the mother is taking care of six other kids.”
Children’s needs, especially young children’s, are left out of climate planning, experts said, because of a lack of advocacy, a lack of funding, a lack of collaboration across government ministries, and a lack of data — conditions which all reinforce each other.
“The child lobby is really lacking,” in international climate negotiations, Zangerl said. A 2023 report from Save the Children found only 2.4 percent of the money from big international climate funds went to projects that incorporated children’s needs.
As a result, research into climate impacts on children isn’t well funded, and this, in turn, impacts decision-making. For example, in Europe where Zangerl lives, there’s an enormous amount of research on elderly people dying in heat waves. Far less is known about children’s morbidity, such as the way heat waves experienced in early childhood might not necessarily end a life, but could shorten a life.
For Zangerl and Akhtar, there are two big arguments for countries to do better at planning for and meeting children’s needs in climate adaptation.
One is that it’s practical and pragmatic. If we want a healthy, resilient adult population to cope with the worsening effects of climate change in 20 years, we need to invest in children today. And most of the world’s children — more than 75 percent of all adolescents — happen to be located in low- and middle-income countries that are more susceptible to the impact of climate.
Education and public health awareness are the most common way that children are being included in these national adaptation plans. This perspective tends to treat children more as a resource to be tapped for the benefit of society, than as a population with needs to be served. Children are being prepared for the green workforce. Or they’re helping disseminate health information.
“In many low- and middle-income countries, the child is the only one who receives formal education,” said Zangerl. “They then teach their wider family and community, and so the multiplier effect of teaching children is really high across the globe.”
The other argument for including children in a country’s climate plans is different. It’s about fairness and children as a more vulnerable population.
“Children are inheriting an over-warmed world, and they will live longer in it than previous generations,” said Akhtar, noting that children will be forced to bear the long-term consequences of decisions made before they were born. “Equipping them with the knowledge and skills to mitigate and adapt is essential to help them survive.”
Zangerl said that when talking about children and climate policy, it’s tempting to keep focused on “risk and vulnerability and protection.” But what’s also important “is agency and empowerment” — having young people as part of the decision-making process on policies that will affect their survival.
“We’re seeing lots of youth advisory boards and adolescents who are change agents or participating actively” in policymaking and activism, she said, noting that it’s possible to listen to even younger children if you are creative about how you do it. For instance, she is currently working on a study with children from ages 3 to 6, where they are making art and taking photos to express how they are coping with changes to weather and nature.
Correction: A previous version of this story misstated the number of countries with climate adaptation plans that mention children.
This story was originally published by Grist with the headline The kids are not alright: Countries fail to include children in their climate plans on Jun 21, 2024.
According to a new global survey of 75,000 people — Peoples’ Climate Vote 2024 — 80 percent want their governments’ climate commitments to be stronger.
The poll, conducted by the United Nations Development Program (UNDP), GeoPoll and Oxford University, posed 15 questions via telephone to residents of 77 countries that represented 87 percent of the global population, reported AFP.
“The Peoples’ Climate Vote is loud and clear. Global citizens want their leaders to transcend their differences, to act now and to act boldly to fight the climate crisis,” said Achim Steiner, UNDP administrator, in a press release from UNDP. “The survey results – unprecedented in their coverage – reveal a level of consensus that is truly astonishing. We urge leaders and policymakers to take note, especially as countries develop their next round of climate action pledges – or ‘nationally determined contributions’ under the Paris Agreement. This is an issue that almost everyone, everywhere, can agree on.”
According to the survey, 89 percent of poorer countries were in favor of increasing efforts to curb global emissions, while 76 percent of wealthy G20 nations supported tougher climate action.
The numbers were a bit lower from the planet’s biggest greenhouse gas emitters, with China at 73 percent and the United States at 66 percent backing more fervent measures to combat global heating.
“As world leaders decide on the next round of pledges under the Paris Agreement by 2025, these results are undeniable evidence that people everywhere support bold climate action. The Peoples’ Climate Vote has enlisted the voices of people everywhere – including amongst groups traditionally the most difficult to poll. For example, people in nine of the 77 countries surveyed had never before been polled on climate change. The next two years stand as one of the best chances we have as the international community to ensure that warming stays under 1.5°. We stand ready to support policymakers in stepping up their efforts as they develop their climate action plans through our Climate Promise initiative,” said Cassie Flynn, UNDP’s global director of climate change, in the press release.
Some of the highest numbers were in Brazil — where 85 percent were in favor of strengthening climate commitments — Iran with 88 percent and Italy with 93 percent.
Among five big emitters — Canada, France, Germany, Australia and the U.S. — women were more in support of stronger climate action by 10 to 17 percent.
The survey also showed a worldwide majority — 72 percent — in support of a fast fossil fuel phaseout, including in nations that are in the top 10 largest coal, oil and gas producers.
Just seven percent of those polled globally thought their government should not transition away from fossil fuels at all.
Climate change is definitely on the minds of people throughout the world. The poll found that 56 percent of people were thinking about it on a regular basis — daily or weekly — with 63 percent of those living in Least Developed Countries (LDCs).
More than half of those polled — 53 percent — also said they worried more about climate change this year than last year.
Worldwide, 69 percent indicated that their big life decisions, such as where to work or live, were impacted by the climate crisis. In LDCs the proportion was higher at 74 percent and lower in Northern and Western Europe at 52 percent and North America at 42 percent.
“A survey of this size was a huge scientific endeavour. While maintaining rigorous methodology, special efforts were also made to include people from marginalised groups in the poorest parts of the world. This is some of the very highest quality global data on public opinions on climate change available,” said Professor Stephen Fisher of University of Oxford’s Department of Sociology in the press release.
The post Four Out of Five People Want Increased Climate Action, UN Poll Says appeared first on EcoWatch.
The derailment of a freight train carrying hazardous materials in East Palestine, Ohio, last year was an environmental disaster.
A new analysis of pollution and precipitation data has found that snow and rain samples collected from the Midwest to Maine and North Carolina after the crash contained high levels of pollutants, including the extremely toxic vinyl chloride, released during a controlled burn to prevent a potential explosion, reported The Guardian.
In all, at least 16 states and southern Canada were affected over an area of 1.4 million square kilometers, AFP reported.
“On 3 February 2023, a Norfolk Southern train derailment occurred in East Palestine, Ohio. The accident and subsequent fire resulted in the emissions of large amounts of hazardous compounds to the ambient atmosphere over many days,” the study said. “About 50 train cars were involved in the accident, of which 38 derailed and at least 11 cars were carrying a variety of hazardous materials… The cargo carried by the involved railroad cars included several volatile organic compounds (VOCs), including vinyl chloride, 2-butoxyethanol, 2-ethylhexyl acrylate, etc.”
The precipitation samples were collected from 260 sites around the country as part of the National Atmospheric Deposition Program (NADP).
Finding high levels of toxic pollutants across such a large area was “very surprising” to the researchers, who had expected to find evidence of the fires from the crash 50 miles away, said lead author of the study David Gay, a researcher at University of Wisconsin and coordinator of NADP, as reported by The Guardian.
“We saw the chemical signal from this fire at a lot of sites and far away,” Gay said. “There was more than we ever would have guessed.”
The smell of chemicals lingered in the town of approximately 4,700 for weeks after the derailment.
Gay said fires burning so long after the crash, as well as the vinyl chloride being so hot and concentrated — which resulted in a tall plume reaching into the strong winds of the planet’s free troposphere — caused the extensive spread of chemical pollution.
“Our measurements not only show the expected high chloride concentrations, but also the vast geographical area they covered,” Gay said, as AFP reported. “However, even more surprising are the unexpectedly high pH levels (more basic) and exceptionally elevated alkali and alkaline earth metals, exceeding the 99th percentiles of the last ten years of measurements. All of these pollutants are important in the environment because their accumulation has an impact on the Earth’s aquatic and terrestrial environments in many ways.”
Gay pointed out that the “exceptionally high” pH levels were found as far afield of the crash as northern Maine, reported The Guardian. Gay said the cargo on the train — including cotton balls, semolina and frozen vegetables — probably contributed to elevated pH levels because large volumes of potassium, calcium and magnesium were released. Firefighting foam used at the site could also have contributed calcium to the high pH.
During the burn a low pressure system moved in across the region, pushing the pollution through Michigan and into Wisconsin. Gay said it was likely that all of the Great Lakes other than Lake Superior were affected.
Chemical pollution levels were elevated for two weeks after the fires, then dropped off the third week.
Gay said this was “further evidence that it’s from the train wreck,” The Guardian reported.
“This study demonstrates the important role of a nationwide network for routine precipitation monitoring,” Gay emphasized, as reported by AFP. “Our observations allowed us to determine the regional atmospheric impact from the accident and subsequent response activities.”
The post Chemicals From 2023 Ohio Train Derailment Spread to 16 States and Canada, Study Finds appeared first on EcoWatch.
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has changed the listing for the Iberian lynx species, or Lynx pardinus, from Endangered to Vulnerable in the organization’s Red List, a list detailing the extinction risk of species around the world.
Francisco Javier Salcedo Ortiz, coordinator of the LIFE Lynx-Connect project that led conservation efforts for the species, described the population rebound as “The greatest recovery of a cat species ever achieved through conservation” in a statement by IUCN.
The change listing follows more than 20 years of recovery efforts to save the Iberian lynx, which had only 62 mature individuals by 2001, CBS News reported. The species was threatened by human activity and habitat loss along with declines in its prey, European rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus). By 2005, the Iberian lynx habitat spanned just 449 square kilometers.
In response, conservationists worked to improve the species’ habitat, including restoring Mediterranean scrub and forest areas, minimizing deaths of the cats from human activities and boosting European rabbit populations in the lynx’s range. Conservationists worked with local communities to reduce lynx deaths from traffic collisions and poaching, CBS News reported.
According to IUCN, scientists also used breeding programs and translocations to improve genetic diversity within the species. More than 400 Iberian lynx have been reintroduced in Portugal and Spain as part of these efforts.
“There is still a lot of work to do to ensure that Iberian lynx populations survive and the species recovers throughout its indigenous range,” Ortiz said. “Looking ahead, there are plans to reintroduce the Iberian lynx to new sites in central and northern Spain.”
In 2022, there were 648 mature Iberian lynx. Today, IUCN estimated that there are more than 2,000 mature individuals, spanning a habitat range of around 3,320 square kilometers.
“The significant recovery of the Iberian lynx demonstrates that even the most threatened species can be brought back from the brink of extinction through committed, science-based conservation action and provides hope for those working to protect wildlife across the globe,” Sarah Durant, professor at the Zoological Society of London’s Institute of Zoology, said in a press release.
While IUCN has changed the status of the Iberian lynx from Endangered to Vulnerable, it also describes the species as Largely Depleted, which means the species will require ongoing conservation actions and protections.
In 2013, a study warned that the Iberian lynx could become extinct in the wild by the 2060s. Now, IUCN said that the species could fully recover in the next 100 years with continued actions toward conservation.
IUCN will publish a comprehensive Red List update for this year on June 27.
The post Iberian Lynx Recovers From Endangered Species Status Following Conservation Efforts appeared first on EcoWatch.
In August 1817, the learned men of the Linnaean Society of New England had studied…
The post Adaptive Management: The Sea Serpent, Organized Growth and Natural Harmony appeared first on Earth911.
James Parravani came down with flu-like symptoms the day before his daughter’s wedding reception. He had a fever, a headache, and chills. It was Labor Day weekend 2021, and his family thought he might have COVID-19. But a test at an emergency room near his home in Westchester, New York, came back negative.
The ER doctors quickly transferred Parravani to Yale New Haven Hospital in Connecticut, where he had received a kidney transplant a year prior. The specialists there suspected he might have a kidney or blood infection related to his operation. They gave him a round of antibiotics, but he just kept getting worse.
Parravani, known to friends and family as Jim, took a long, winding road to his daughter’s wedding weekend. He dropped out of high school in Schenectady, New York, before his senior year to focus on other priorities. “Rocktoberfest” — a music festival he and his friends threw in a rented-out motel — occupies a near-mythical place in modern Schenectady history. Parravani eventually earned his GED and attended Syracuse University’s College of Law, where he rose to second in his class.
After marrying his middle school sweetheart in 1986, Parravani graduated from law school, moved to Westchester, and began building a career and a family. But in the ’90s, he learned he had a genetic condition called polycystic kidney disease — an illness that causes cysts to grow on the kidneys and often results in organ failure. After several years of treating his cysts, Parravani’s doctors initiated the laborious process of getting him a transplant. In 2020, about a year before his daughter’s wedding weekend, he finally got one.
Now, his doctors thought this transplanted kidney might be making him sick, though they still didn’t know how. The morning of her reception, Jenny Parravani Davis called her dad at the hospital. She asked him if he wanted her to postpone the festivities. “No, no,” he told her. “Keep going.”
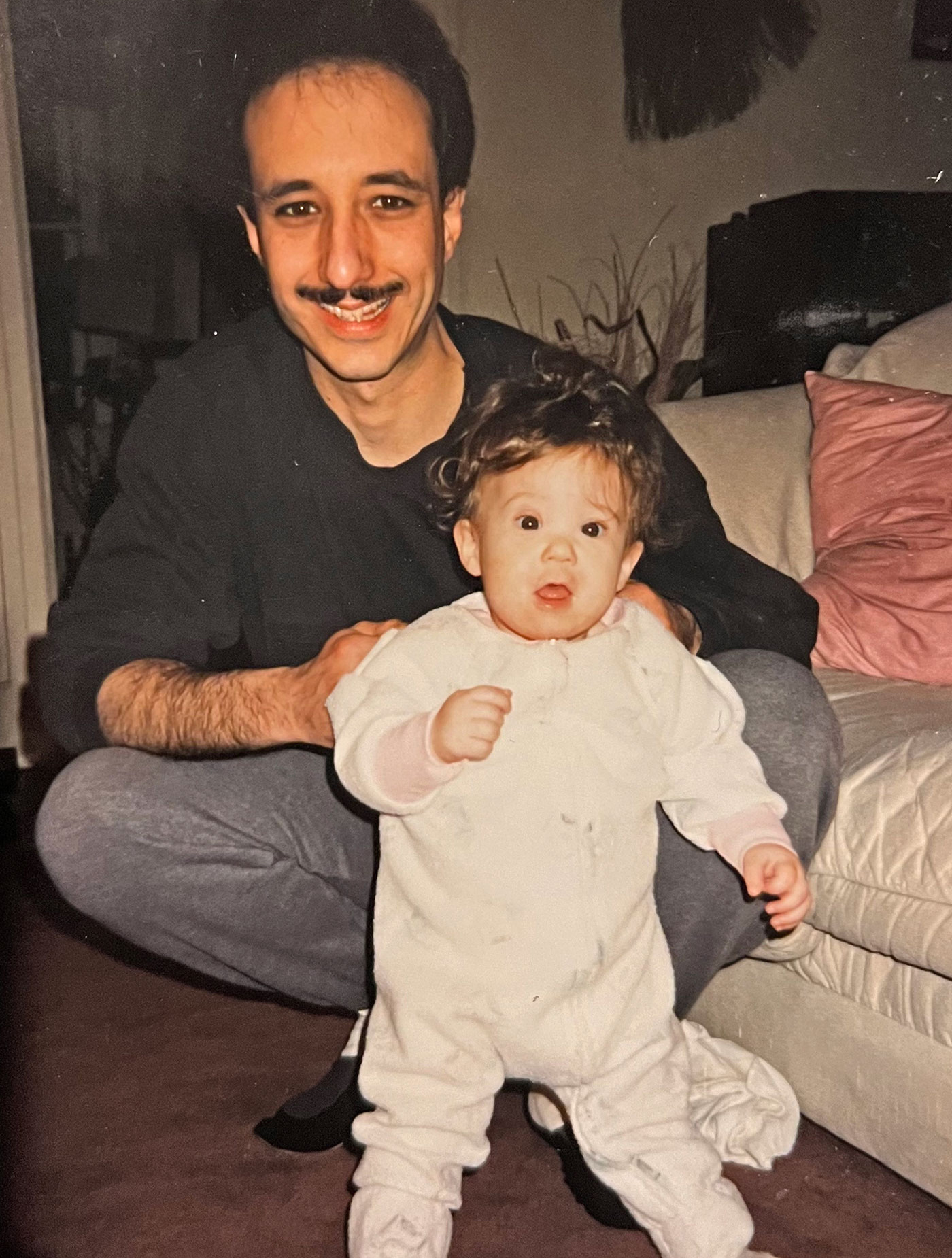
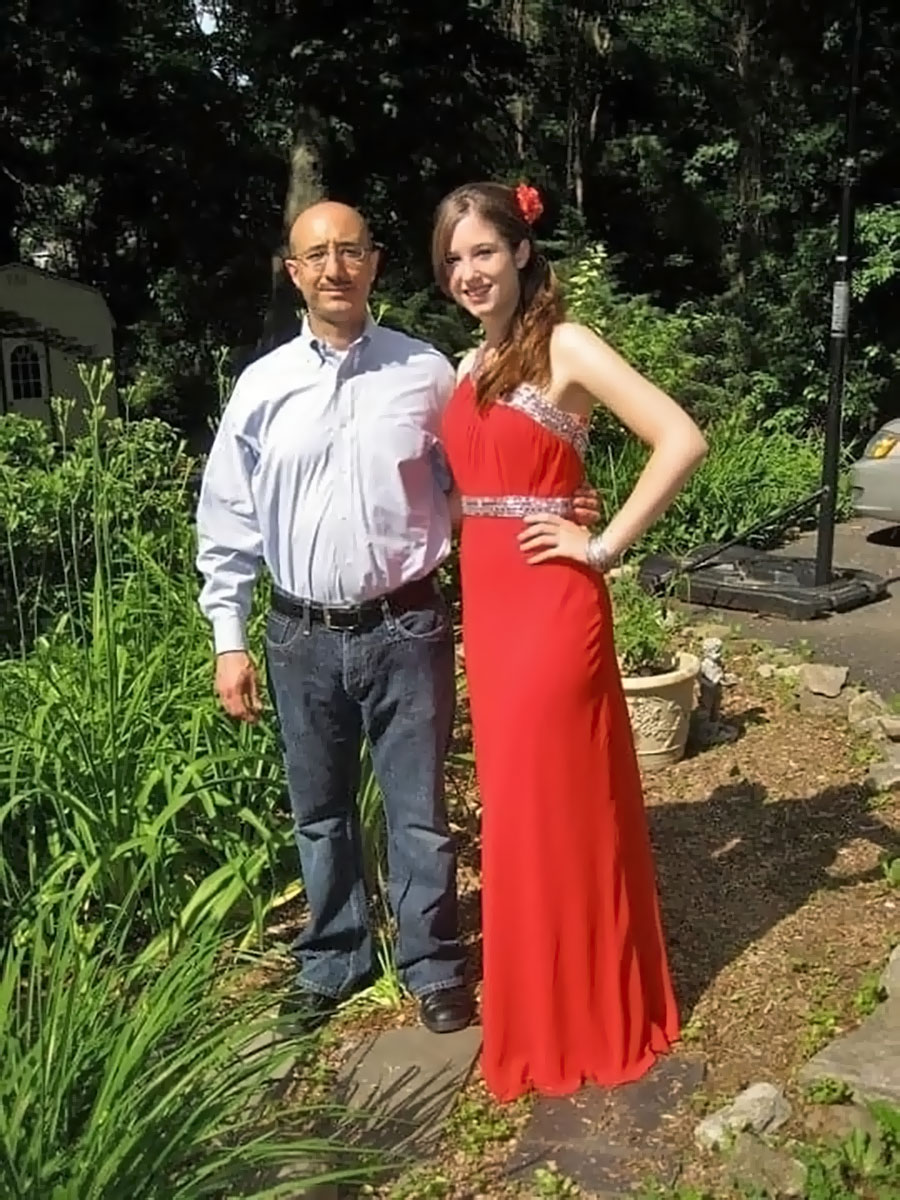


From left: Jim Parravani with his daughter, Jenny, as a toddler. Father and daughter on Jenny’s prom night. Courtesy of Jenny Parravani Davis
That was the last lucid conversation Davis ever had with her father. The next day, she got a call from her mother. Parravani was deteriorating — fast.
“He got on the phone and he was really disoriented, he couldn’t form words,” Davis said. “I remember saying ‘Hi, I love you,’ and he just said, ‘Don’t cry,’ and everything after that was incoherent.” Parravani was intubated that same day.
The doctors ran dozens of tests and put Parravani on multiple courses of strong antibiotics to treat the infection. It was only when they conducted a spinal tap — about a week after Parravani’s initial admission — that they discovered the true culprit: West Nile virus was present in his cerebrospinal fluid. The disease had spread to his brain and was making it swell. (Yale New Haven Hospital declined to comment on Parravani’s care.)
For seven months, as Parravani slipped in and out of comas, the doctors tried to beat back the virus with intravenous fluids, pain medication, and oxygen. At one point, it looked like Parravani might pull through. He was nodding and trying to communicate with his family around his breathing tube. The doctors reduced the oxygen flowing through his ventilator, and he breathed on his own. But in March 2022, Parravani began to decline again. On April 13, Parravani died in hospice care. He was 59 years old.
West Nile has been the most common mosquito-borne illness in North America for more than two decades. States in the Great Plains and western U.S. typically report the highest number of cases, though outbreaks have happened in nearly every state in the continental U.S. The disease has killed more than 2,300 people since it first arrived here, and the number of people affected by the virus every year is poised to rise.
As climate change extends warm seasons and spurs heavier rainstorms, the scope and prevalence of West Nile virus is shifting, too. Warmer, wetter conditions allow mosquitoes to develop more quickly, stay active beyond the traditional confines of summer, and breed more times in a given year. Birds, which host West Nile virus and pass it onto mosquitoes that bite them, are adjusting their migration patterns in response to the melding seasons.
The confluence of these two trends could have serious consequences for human beings. West Nile virus, a recent study said, “underlines once again that the health of animals, humans, and the environment is deeply intertwined.” In the past few years, Colorado and Arizona recorded outbreaks of the virus that killed scores of people in each state. Parts of California and Wyoming also reported unusually high cases of the disease. Meanwhile, Nevada, Illinois, and New York registered above-average or record-breaking numbers of West Nile-infected mosquitoes and mosquito activity.
“Overall, the evidence points to higher temperatures resulting in more bird-mosquito transmission and more what we call spillover infections to people,” said Scott Weaver, chair of the department of microbiology and immunology at the University of Texas Medical Branch.
West Nile virus typically leaves young, healthy individuals unscathed. Only 1 in 5 people who contract it develop symptoms, which can include fever, headache, joint pain, diarrhea, and other signs of illness that often resemble the flu.
There is no cure for West Nile virus; the immune system must fight it off on its own. That’s why elderly people and those with preexisting conditions, such as cancer, diabetes, and kidney disease, are at much higher risk of developing the severe form of the disease. So are organ transplant recipients, who take immunosuppressants for their entire lives to ensure the body does not reject the organ.
About 1 in 150 people who get West Nile develop the worst form of the illness, in which the virus attacks the central nervous system. For 10 percent of these patients — including Parravani — encephalitis or meningitis, swelling of the tissues around the brain and spinal cord respectively, leads to death.

Because only a sliver of infected people get seriously sick, the impact of West Nile virus on the public hinges on the number of people who contract the disease. Some years, the number of infections detected in the U.S. approaches 10,000. Other years, there are fewer than 1,000 reported cases. The number depends in large part on environmental conditions — how much rain fell, how warm or cold the spring or fall was — in addition to bird migration patterns and human behavior.
“It’s a rare event that any given mosquito bites a bird and then survives long enough to bite a human” and transmit West Nile virus, said Shannon LaDeau, a disease ecologist at the Cary Institute of Ecosystem Studies. But as with COVID-19, the size of the denominator is crucial. “When you have millions of mosquitoes, that rare event happens more frequently.” LaDeau said.
Parravani’s illness wasn’t the first case of West Nile to stump medical professionals in the U.S. In August 1999, people in the New York City metropolitan area started becoming severely ill with encephalitis. The patients had previously been healthy and reported being outside in the days leading up to their illness. The New York City Department of Public Health suspected a disease spread by mosquitoes was behind the outbreak and immediately launched an investigation.
In the months before the outbreak, researchers in New York had detected an unfamiliar type of single-stranded RNA virus in some of North America’s wild birds. Birds of prey and members of the crow family, in particular, were dying in unusually high numbers. Four weeks after the people in New York got sick, the chief pathologist at the Bronx Zoo connected the dots and sounded the alarm. The birds were infected with West Nile virus, named after the district in northern Uganda where the disease was first isolated in a human more than half a century earlier. And West Nile, public health authorities eventually confirmed, was what was making New Yorkers sick.
By the end of the summer, 59 people had been hospitalized with West Nile virus. Seven died.
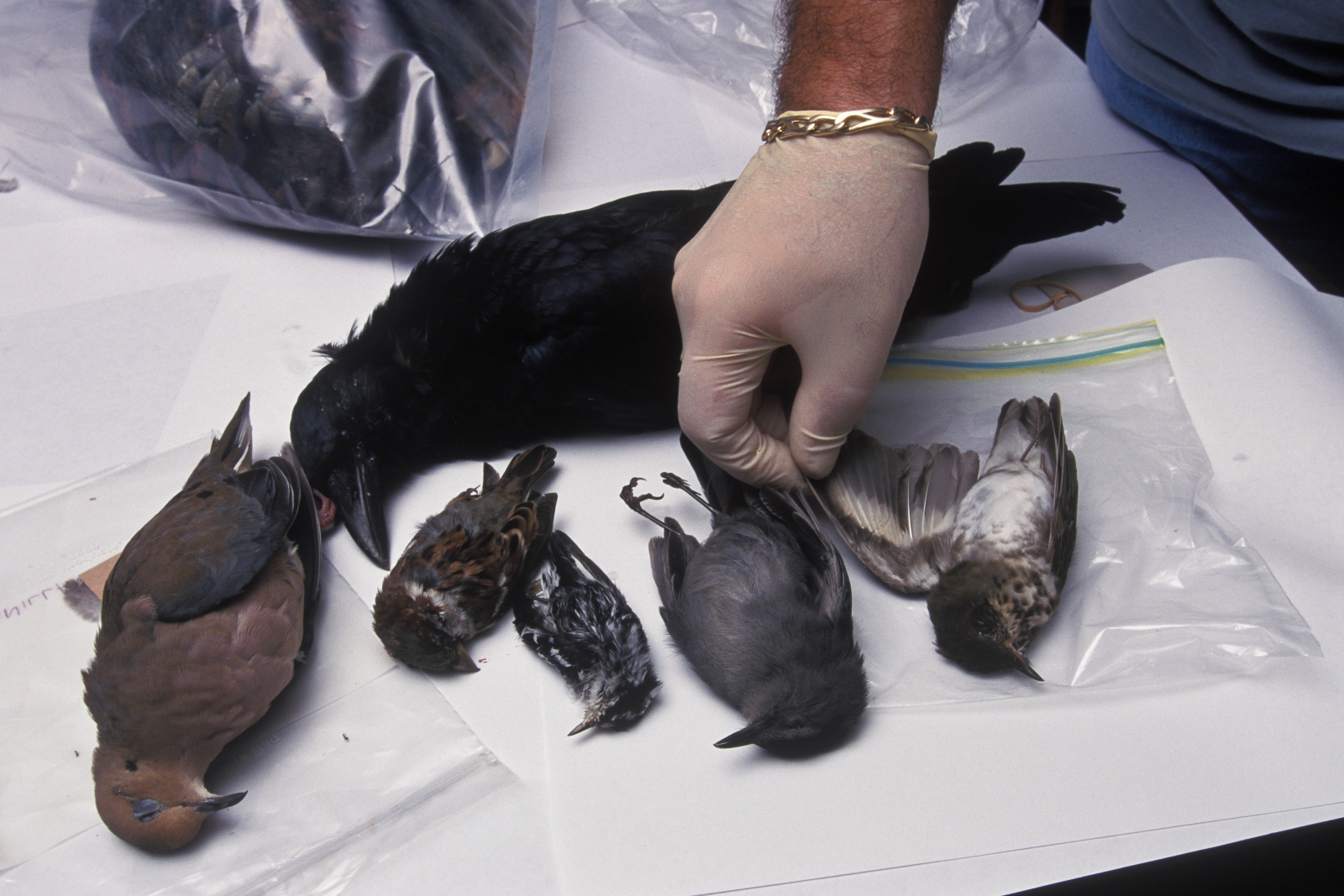

West Nile had been known for decades to cause fever, vomiting, headache, and rashes. Epidemics in the Middle East in the early 1950s helped researchers confirm that the Culex genus of mosquito — dawn and dusk biters that prefer to feed on birds — were the primary vector, or carrier, of the disease. Outbreaks of varying severity cropped up all over the world — in France, India, Israel, Italy, Morocco, Romania, Russia, South Africa, Spain, and Tunisia. But it wasn’t until 1999 that researchers understood that migratory birds could spread the virus from one hemisphere to another.
Once public health officials learned what was behind the encephalitis outbreak in New York, they sprayed pesticide and larvicide around the city to kill mosquitoes. But the disease couldn’t be eradicated. Within three years, birds had carried it from coast to coast and throughout much of Canada.
The public health response to West Nile virus in the U.S. since the turn of the century has been punctuated by successes and setbacks. Every few years, when environmental conditions allow Culex populations to boom, cases careen out of control and hundreds of people die. States and cities often belatedly deploy weapons from a limited arsenal — pesticide-spraying and public awareness campaigns — to keep the disease in check. After a boom year, the next one often brings a different cocktail of environmental conditions, and the disease has a much smaller impact on public health.
“There are many things that go into what causes the circulation of West Nile,” said J. Erin Staples, a medical epidemiologist at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or CDC. “And that makes it very difficult for us to predict.”
The unpredictability of the virus is part of what explains the lackluster response by states and the federal government to the threat of West Nile. No vaccine or cure exists, and funding for research on the disease is low, despite the fact that the virus has been claiming lives in North America for a quarter of a century. “Although West Nile virus continues to cause significant morbidity and mortality at great cost, funding and research have declined in recent years,” a 2021 study said. The National Institutes of Health directed $67 million to West Nile research between 2000 and 2019 — less than a tenth of the $900 million it dedicated to research on Zika, a mosquito-borne illness that never gained a foothold in the U.S., in the same period.
Experts warn that climate change is creating more opportunities for West Nile to spread.
Culex mosquitoes thrive in temperate, wet weather. Like other mosquitoes, they lay their eggs in standing pools of water. The eggs can’t survive below about 45 degrees Fahrenheit, but as temperatures get warmer from there, the time between hatching and reproducing gets shorter. The mosquitoes’ ideal temperature for survival ranges from 68 to 82 degrees Fahrenheit, depending on the precise species, but one Culex species can spread West Nile when it’s anywhere between 57 and 94 degrees F outside.
As temperatures rise and make fall, winter, and spring milder, Culex mosquitoes will have more chances to reproduce and spread West Nile in places that didn’t used to see so many mosquitoes. Meanwhile, because a warmer atmosphere holds more water, extreme rain events are getting more common — and that means more standing water for mosquitoes to breed in.
In New York, where winters are warming three times faster than summers, mosquitoes are now active deep into the month of November. A few decades ago, an adult mosquito flying around past the middle of October would have been highly unusual. “We are starting to see and will continue to see shifts in the range” of West Nile virus, said Laura Harrington, an entomology professor at Cornell University, “and shifts in some of the avian hosts that are most important.”
Climate change also pushes birds into new areas, because of weather changes and adjustments in where and when different types of plants and trees grow and bloom. “There are changes to the habitat where birds migrate to breed every year in the Northern Hemisphere,” said Weaver, the University of Texas microbiologist. “And just the temperature itself may have an impact on migration.” As birds enter new habitats, they have the potential to bring West Nile with them.
There’s already evidence that climate change is fueling West Nile outbreaks. In 2021, Maricopa County, Arizona, got an unusual amount of rain — 6.6 inches between June and September, compared to the 2.2 inches it usually gets during that period. That summer, Maricopa County experienced a historic surge of West Nile virus — the worst outbreak in a U.S. county since the disease arrived 25 years ago. Roughly 1,500 people were diagnosed, 1,014 were hospitalized, and 101 people died. The previous year, the number of recorded cases in the region was in the single digits.
A determining factor in the outbreak, Staples said, was the unusual amount of rain. It led to “an unprecedented increase in the mosquitoes and the ability of that virus to then spread to people.” Arizona is projected to get more bouts of extreme rainfall as the planet warms.
To prevent West Nile outbreaks, public health officials must monitor mosquitoes and birds for the virus. But the behavior of mosquitoes makes surveillance complicated — trickier even than tracking other vectors of disease, such as ticks. Unlike ticks, which stay more or less put, mosquitoes can travel a mile or two in any direction. That means public health agencies must launch an expensive and time-consuming hunt for the bugs, using field tests, maps, and guesswork to figure out where mosquitoes are hiding. Birds are mobile, too, and that further complicates efforts to track, map, and control the disease.
Even accounting for these challenges, epidemiologists say too few states are deploying sufficient effort and resources to make sure that they are able to predict and respond to outbreaks of West Nile virus. “We still are using the same vector control and the messaging to use your insect repellant that we were using 25 years ago,” Staples said.
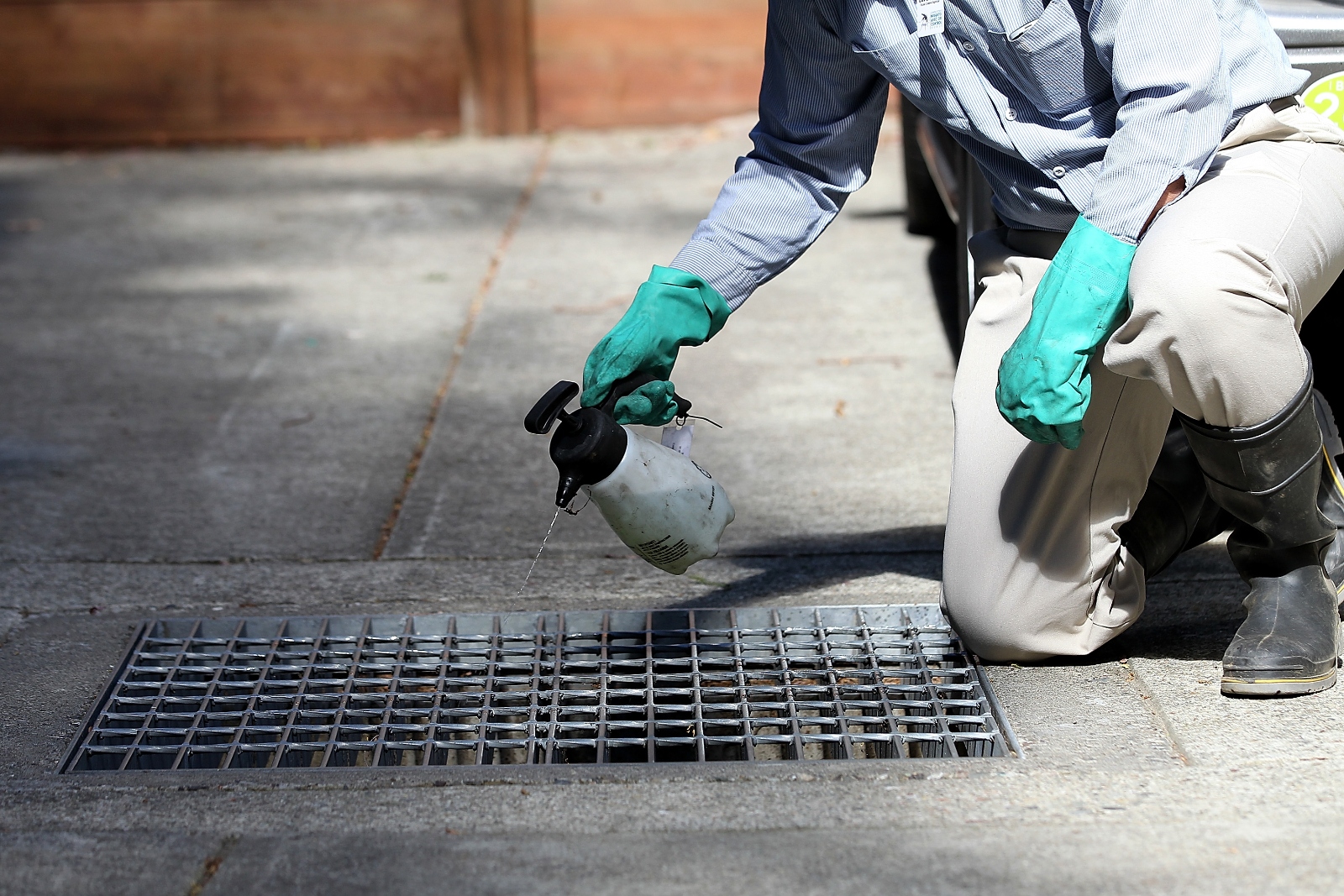

Some states are doing a better job than others. Massachusetts and New York, among the most aggressive states in the nation when it comes to tracking West Nile virus, test mosquito breeding sites and birds regularly and, when positives come back, use that information to inform the public. After Parravani’s spinal tap revealed that he had West Nile, the Westchester County Health Department went to his house and conducted a sweep of the property. County public health officials drained pools of standing water in the backyard where the mosquitoes had likely bred, and they encouraged nearby residents to do the same on their own properties.
“In some places there’s a very clear link that guides when you test and what you test for,” LaDeau said. But “mosquito surveillance is not the norm across all regions, and it’s not standardized among even regions within a state.”
As climate change loads the dice in favor of mosquitoes, West Nile is not the only infectious illness in flux. The number of cases of vector-borne disease in the U.S. have more than doubled since 2001. Some of that increase can be attributed to better disease awareness among physicians and the public, and an uptick in testing as a result. But there are also examples of diseases bursting out of the regions where they have historically been found, which may be an indication that changes in the environment are coaxing carriers of disease into new places.
In 2023, the U.S. saw the first-ever cases of locally transmitted dengue fever in Southern California and unusual cases of locally acquired malaria in Texas, Florida, and Maryland. When a mosquito imparts West Nile virus to a human, the transmission of the virus stops there. An infectious human cannot infect a mosquito with the virus. That’s not the case for dengue and malaria, which makes the spread of those diseases potentially far more dangerous.
Many studies show that infectious diseases will take a larger toll on public health across North America as we make our way deeper into the 21st century. “More Americans are at risk than ever before,” Christopher Braden, the acting director of the CDC’s Center for Emerging and Infectious Zoonotic Diseases, warned in 2022.
If West Nile virus, the nation’s most common mosquito-borne illness, is a test for how the U.S. will weather the coming influx of vector-borne disease, then the country is in bad shape. “We don’t have very good tools to control it and prevent human illness,” Harrington said.
For now, however, those who have been personally impacted by mosquito-borne illnesses are arming themselves with DEET and ringing the alarm. Until recently, Jenny Parravani Davis worked as a communications manager for the Wilderness Society, a land conservation organization that advocates for better protection of the nation’s remaining wild places. The climate change reports that the Wilderness Society puts out generally include top-line findings about the ways in which climate change will erode human health as temperatures rise. But her father’s death, Davis said, drove home just how interconnected these issues really are.
“I started to connect the dots and see the bigger picture,” she said. Her backyard in Virginia collects a lot of water, especially in recent years, as back-to-back record-setting rain events have flooded the state. “I don’t think anyone would blame me, but I’ve developed this neurosis where anytime I scratch a mosquito bite I’m like, ‘Could this be the thing that kills me today?’” she said. “I’ve seen what happens when we don’t pay attention to these things.”
Correction: This story originally misstated Jenny Parravani Davis’ first name.
This story was originally published by Grist with the headline When West Nile virus turns deadly on Jun 20, 2024.
Just a few weeks into the hurricane season, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA, has declared the end of El Niño, the warm streak of water in the Pacific that influences global weather. That makes an already dire outlook for cyclones even more dangerous — in April, scientists forecasted five major hurricanes and 21 named storms in the North Atlantic alone — because El Niño tends to suppress the formation of such tempests.
NOAA now predicts a 65 percent chance of La Niña, which is favorable for cyclones, developing between July and September, when such events are most common. (La Niña is a band of cool water forming in contrast to El Niño’s warm band.) At the same time, sea surface temperatures remain extraordinarily high in the Atlantic — the kind of conditions that power monster storms.
The Atlantic is primed for a brutal hurricane season. But these cyclones aren’t just made of devastating winds and rains — they’re full of invaluable data that scientists will use to improve forecasting, giving everyone from local meteorologists to federal emergency planners better information to save lives.
Such insights would be particularly critical if, for instance, a hurricane rapidly intensifies — defined as an increase in sustained wind speeds of at least 35 mph in 24 hours — just before it reaches shore and mutates from a manageable crisis into a deadly one. “Those cases right before landfall, where people are most vulnerable, is the nightmare scenario,” said Christopher Rozoff, an atmospheric scientist at the National Center for Atmospheric Research who models hurricanes. “That’s why it’s of such great interest to improve this, and yet it’s been a huge forecasting challenge until somewhat recently.” (Which is not to say weaker storms can’t also be catastrophic — for instance, they might stall over a city and dump torrential rain.)
For such calamitous phenomena, hurricanes feed on a certain level of atmospheric boringness. El Niño suppresses the development of these storms by encouraging vertical wind shear, or winds moving at different speeds and directions at different elevations. That messiness tilts the vortex, interfering with a hurricane’s ability to spin up uniformly. The La Niña that could form this summer, on the other hand, decreases that wind shear in the Atlantic, providing ideal conditions for cyclones.
On the ocean’s surface, extremely high temperatures have already turned the Atlantic into a vast pool of fuel for hurricanes to start forming. When this water evaporates, the vapor is ingested by the storm, forming buoyant clouds that release heat and lower the atmospheric pressure. This draws in air to create wind, which spins up into a vortex.
If the sea is warm enough, and vertical wind shear is low enough, a hurricane has the potential for rapid intensification. “The atmosphere usually drives the bus when it comes to rapid intensification — it is definitely something that is on my mind this hurricane season,” said Eric Blake, a senior hurricane specialist at the NOAA’s National Hurricane Center. “When you have extremely warm waters, it just increases the chances that it can occur in areas that maybe it wouldn’t normally occur in.”
Last year, several hurricanes quickly strengthened, including Hurricane Idalia, which tore into communities along the Florida coast. Over in the Pacific, Hurricane Otis evolved into a monster with stunning speed before devastating Acapulco, Mexico. “That storm intensified from a tropical storm to a Category 5 in just over a 24-hour period,” said Rozoff. (For context, a Category 1 hurricane has sustained winds of at least 74 mph, while Category 5 is at least 157 mph.) “We’ve seen improvements in forecasting and our ability to capture these events, but that particular forecast still fails, unfortunately, by the numerical models. None of them were foreseeing this intensification to such an extreme storm that would be so damaging.”
Because blistering strengthening involves highly complicated interactions between the sea and the sky, it’s notoriously hard to predict. As the planet warms, hotter oceans provide more energy for hurricanes, and complex ripple effects across the atmosphere might also reduce wind shear along the Atlantic coast going forward. Indeed, a paper published last year found an explosion in the number of rapid intensification events close to shore in recent decades.
Not only are scientists trying to parse why a particular hurricane would quickly intensify in 2024, they have to figure out what to expect as the oceans get hotter and hotter, providing more and more cyclone fuel. It’s a moving target, one made of torrential rain and 160 mph winds. “We have a great database of weather that happens now, and we don’t necessarily have a great database of weather that will happen in the future,” said Sarah Gille, a physical oceanographer at the Scripps Institution of Oceanography. “So extreme storms are one window into that, that can help us get a better picture of what we might see.”
As hurricanes spin across the Atlantic this summer, scientists will be ready. They can fly “Hurricane Hunter” aircraft into the cyclones while collecting oodles of data like wind speed, pressure, and humidity. (That’s another factor in major hurricanes: They love humidity and hate dry air.) They’ll then feed this data into models that try to predict rapid intensification. Increasingly, scientists are using artificial intelligence to supercharge these algorithms, for instance training an AI to recognize patterns in satellite images of a hurricane, or precipitation in the core of the storm, to predict whether it will rapidly intensify or not.
Whether from an aircraft or a satellite, every new observation of these cyclones feeds into models that are getting better at understanding why hurricanes behave the way they do. That means better information for coastal cities to decide whom to evacuate and when. “We’ve gotten a lot of good data at a time when the technology is improving, so I think that’s why we’ve made so much progress,” said Rozoff. “Every case of rapid intensification before landfall — whether forecasted well or not — is a tragedy, or at least a serious challenge for humanity. But it has provided us some good data as well.”
This story was originally published by Grist with the headline How this summer’s brutal hurricanes might one day save lives on Jun 20, 2024.
A new study has found that approximately one in four households in the United States has soil lead levels exceeding the new U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)’s limit of 200 parts per million (ppm). The previous screening level was 400 ppm.
For households that have multiple sources of lead exposure, the guidance level was lowered to 100 ppm, a press release from the American Geophysical Union (AGU) said. The researchers found that almost 40 percent of households in the United States exceeded that level.
“Based on a wide network of citizen-science collected household soil samples, we find that nearly one in four households may now contain a soil lead hazard based on this new, more protective standard,” the authors of the study wrote. “Unsafe levels of lead exposure [have] occurred in many communities across the United States, with much of the burden resting on lower income communities, and communities of color. Lead exposure is prevalent due to past lead emissions and the substantial legacy lead loads that remain in soils and structures within communities.”
A lead concentration limit for human blood was first set by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention back in 1991, AGU said. However, the lead screening level for soil set by the EPA was the same for more than three decades until early this year. By then, some states like California — which has the lowest limit at 80 ppm — had established their own guidelines.
In the study, the authors said the delay was likely due to “the immensity and ubiquity of the problem.”
“The scale is astounding, and the nation’s lead and remediation efforts just became substantially more complicated,” the authors said. This is because the lower limits mean the EPA needs to let people know the steps to take if their soils are over the appropriate threshold.
To find out how many households exceeded the updated guidelines, the researchers looked at their database of residential soil samples — 15,595 of them — collected from gardens, yards, alleys and other residential locations across the contiguous U.S.
They found that about a quarter of the samples exceeded the new limit of 200 ppm, whereas just 12 percent had exceeded the higher threshold of 400 ppm. That means about 29 million households across the country exceed the new lead limits.
For households with multiple exposure sources — like lead pipes and soil contaminated with lead — the EPA guidance level is 100 ppm. According to the study, 40 percent of households were above that limit, bringing the number to nearly 50 million.
“I was shocked at how many households were above the new 200 ppm guideline,” said Gabriel Filippelli, lead author of the study and an Indiana University biochemist, in the press release. “I assumed it was going to be a more modest number. And results for the 100 ppm guideline are even worse.”
The study, “One in Four US Households Likely Exceed New Soil Lead Guidance Levels,” was published in the journal GeoHealth.
Lead, a heavy metal, can build up in the human body and have toxic effects. It can come from old paint and water pipes, industrial pollution and remnant gasoline. Most lead exposure today is from contaminated dust and soils that remain after the removal of lead-tainted infrastructure.
In the U.S., there is a historically disproportionate burden of lead exposure in communities of color and those with lower incomes due to discriminatory practices such as redlining — a real estate practice where financial services were withheld in neighborhoods with higher numbers of ethnic and racial minorities. Lead exposure has been linked with lower educational outcomes in children.
Contaminated soils are usually remediated with traditional “dig and dump” removal, but this method is costly and requires an area to first be put on the remediation National Priority List, which can be a years-long process. The researchers calculated that the remediation of all contaminated households using the “dig and dump” method would cost from $290 to $1.2 trillion.
The process of burying lead-contaminated soil with roughly a foot of mulch or soil — called “capping” — is a less expensive option. The installation of a geotechnical fabric barrier is also a potential solution.
Filippelli pointed out that most soil lead contamination sits in the first 10 to 12 inches underground, so either of these methods dilutes or covers up the issue to a level that is acceptable.
“Urban gardeners have been doing this forever anyway, with raised beds, because they’re intuitively concerned about the history of land use at their house,” Filippelli said. “A huge advantage of capping is speed. It immediately reduces exposure. You’re not waiting two years on a list to have your yard remediated while your child is getting poisoned. It’s done in a weekend.”
Filippelli emphasized that despite the time and effort it takes to cap soil, the costs are likely outweighed by the health benefits. There is still a lot that is unknown about the sustainability and lifespan of capping, Filippelli added, and that will be a focal point of research in the future.
“I’m really optimistic,” Filippelli said in the press release. “Lead is the most easily solvable problem that we have. We know where it is, and we know how to avoid it. It’s just a matter of taking action.”
The post 1 in 4 Yards in U.S. Exceeds New EPA Limits for Lead Levels in Soil, Study Finds appeared first on EcoWatch.