The spotlight
It’s no secret that climate change poses a threat to our agricultural systems. Hotter temperatures and shifting rainfall patterns, as well as extreme weather events, are already placing stress on farms and imperiling our ability to grow certain crops in certain places. Some of the first casualties will likely be sensitive, specialty crops, like the tropical berries that make one of the world’s most beloved beverages: coffee.
But as long as coffee has been around, alternatives have cropped up around it. And today, a new wave of startups is entering the coffee-imitation game, motivated by the threat climate change poses to the world’s coffee supply.
“I was surprised by just how many types of coffee alternatives are out there,” said L.V. Anderson, a senior editor at Grist who explored these alternatives, grouped under the banner of “beanless coffee,” in a feature story last week. “There’s a really strong tradition, in nearly all regions around the world, of making these brewed beverages that have a resemblance to coffee.”
That tradition has often been driven by cost — offering cheaper options, like toasted barley and rye, for the masses who couldn’t afford a specialty item like coffee. And that’s part of the calculus for today’s climate-focused startups as well, which are making coffee substitutes from readily available ingredients, including various pits, roots, seeds, grains, and legumes. As climate change threatens coffee production, it is likely to drive up the price of the real deal, which could fuel demand for affordable alternatives.
But of course, for those alternatives to begin to gain a foothold today, they have to be good.
When Anderson first began reporting the story, “as someone who drinks coffee and is attached to coffee,” she was highly skeptical of what these startups were offering. “I’m not a morning person, and coffee is really important to me to actually, like, wake up and be ready to face the day,” she said. But her editor encouraged her to approach the story with an open mind, which she did — even sampling a couple of the brews.
While she enjoyed them, for the most part, she was keenly aware that they were not coffee. The rich, seductive smell was missing, and the taste was “just slightly off in a way that’s hard to put your finger on,” Anderson said. But, she added, she could see herself getting used to them if she had to.
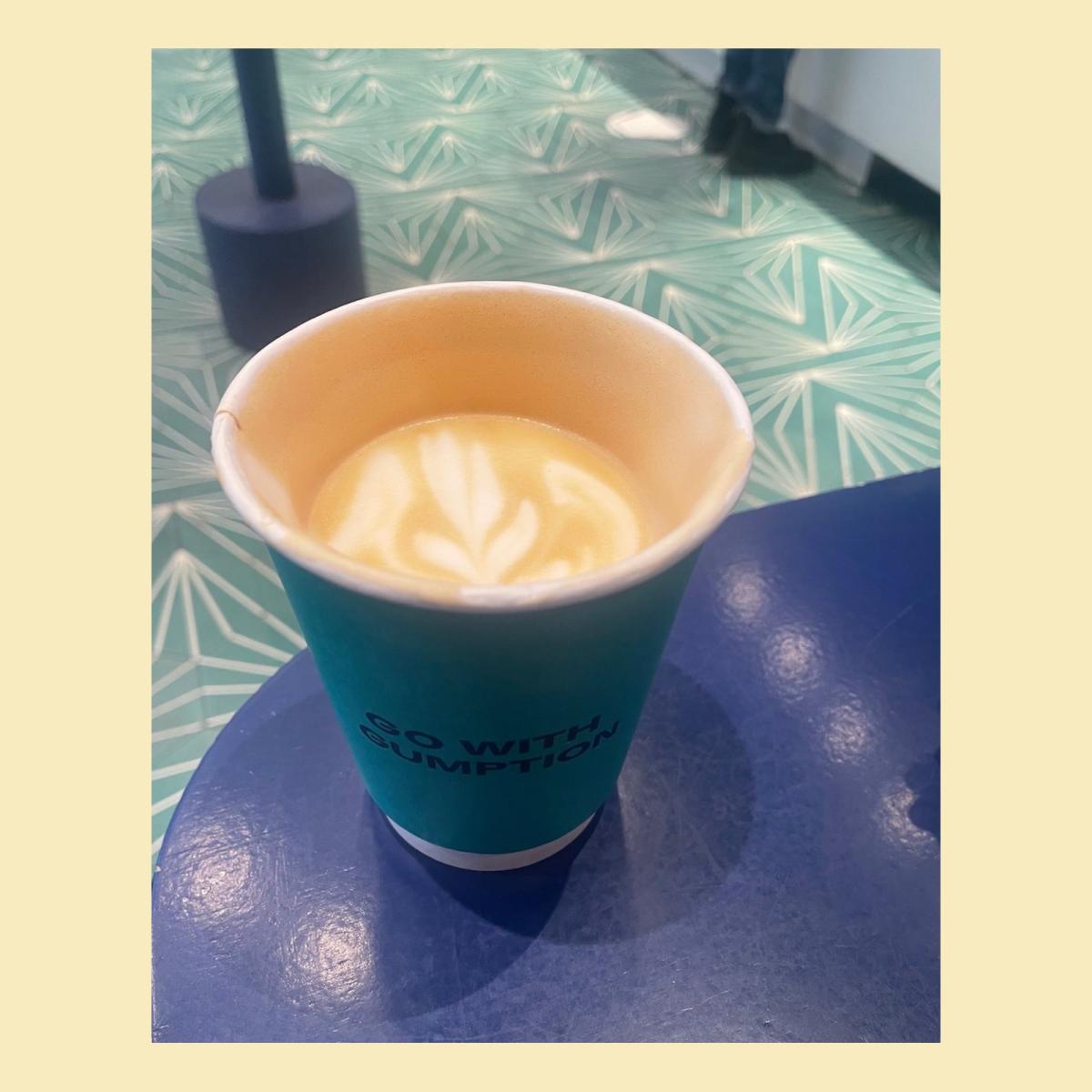

A latte that Anderson tried at Gumption Coffee in Manhattan, made with beanless grounds from a company called Atomo. L.V. Anderson / Grist
Although coffee is not one of the worst offenders when it comes to the climate impacts of agriculture (like beef and dairy, two other products that have grown their own markets of alternatives), its production does come at an ecological cost. And in many cases, these coffee-less coffee companies are appealing to sustainability-conscious consumers by offering what they claim to be a more eco-friendly option. “I think pretty much all these companies, or most of them at least, are making claims about how their product is deforestation-free,” Anderson said. At least a few startups are also focusing on agricultural waste products to make their brews, helping to keep food waste out of landfills.
These companies may be hoping that early adopters will make the switch based on this sustainability argument, but ultimately, Anderson said, they’re also making a bet that these products will be more climate-proof than real coffee — and that coffee lovers, like Anderson herself, may end up being willing to adjust to the dupes.
“I can’t make predictions about what’s going to happen in the future,” she added, “but I do find it plausible, this vision that beanless coffee companies are pitching for the future — which is that coffee is just going to get really expensive, and it’s going to be hard for people to access coffee the way that they’re used to accessing it.”
In the excerpt below, Anderson explains how beanless coffee is actually brewed, and some of the many many coffee alternatives that are hitting the market. Check out the full piece on the Grist site.
— Claire Elise Thompson

The best coffee for the planet might not be coffee at all (Excerpt)
Coffea arabica — the plant species most commonly cultivated for drinking — has been likened to Goldilocks. It thrives in shady environments with consistent, moderate rainfall and in temperatures between 64 and 70 degrees Fahrenheit, conditions often found in the highlands of tropical countries like Guatemala, Ethiopia, and Indonesia. Although coffee plantations can be sustainably integrated into tropical forests, growing coffee leads to environmental destruction more often than not. Farmers cut down trees both to make room for coffee plants and to fuel wood-burning dryers used to process the beans, making coffee one of the top six agricultural drivers of deforestation. When all of a coffee tree’s finicky needs are met, it can produce harvestable beans after three to five years of growth, and eventually yields 1 to 2 pounds of green coffee beans per year.
If arabica is Goldilocks, climate change is an angry bear. For some 200 years, humans have been burning fossil fuels, spewing planet-warming carbon dioxide into the air. The resulting floods, droughts, and heat waves, as well as the climate-driven proliferation of coffee borer beetles and fungal infections, are all predicted to make many of today’s coffee-growing areas inhospitable to the crop, destroy coffee farmers’ razor-thin profit margins, and sow chaos in the world’s coffee markets. That shift is already underway: Extreme weather in Brazil sent commodity coffee prices to an 11-year high of $2.58 per pound in 2022. And as coffee growers venture into new regions, they’ll tear down more trees, threatening biodiversity and transforming even more forests from carbon sinks into carbon sources.
At many times in the past, coffee has been out of reach for most people, so they found cheaper, albeit caffeine-free, alternatives. Caro and other quaint instant beverage mixes, like Postum in the U.S. and caffè d’orzo in Italy, were popular during World War II and in the following years, when coffee was rationed or otherwise hard to come by. But the practice of brewing non-caffeinated, ersatz coffee out of other plants is even older than that. In the Middle East, people have used date seeds to brew a hot, dark drink for hundreds or perhaps thousands of years. In pre-Columbian Central America, Mayans drank a similar beverage made from the seeds of ramón trees found in the rainforest. In Europe and Western Asia, drinks have been made out of chicory, chickpeas, dandelion root, figs, grains, lupin beans, and soybeans. These ingredients have historically been more accessible than coffee, and sometimes confer purported health benefits.

An illustrated advertisement from 1902 for Postum by the Postum Cereal Company of Battle Creek, Michigan. Jay Paull / Getty Images
Today’s beanless-coffee startups are attempting to put a modern spin on these time-honored, low-tech coffee substitutes. Northern Wonder, based in the Netherlands, makes its product primarily out of lupin beans — also known as lupini — along with chickpeas and chicory. Atomo, headquartered in Seattle, infuses date seeds with a proprietary marinade that produces “the same 28 compounds” as coffee, the company boasts. Singapore-based Prefer makes its brew out of a byproduct of soymilk, surplus bread, and spent barley from beer breweries, which are then fermented with microbes. Minus also uses fermentation to bring coffee-like flavors out of “upcycled pits, roots, and seeds.” All these brands add caffeine to at least some of their blends, aiming to offer consumers the same energizing effects they get from the real deal.
“We’ve tried all of the coffee alternatives,” said Maricel Saenz, the CEO of Minus. “And what we realize is that they give us some resemblance to coffee, but it ultimately ends up tasting like toasted grains more than it tastes like coffee.”
In trying to explain what makes today’s beanless coffees different from the oldfangled kind, David Klingen, Northern Wonder’s CEO, compared the relationship to the one between modern meat substitutes and more traditional soybean products like tofu and tempeh. Many plant-based meats contain soybeans, but they’re highly processed and combined with other ingredients to create a convincing meat-like texture and flavor. So it is with beanless coffee, relative to Caro-style grain beverages. Klingen emphasized that he and his colleagues mapped out the attributes of various ingredients — bitterness, sweetness, smokiness, the ability to form a foam similar to the crema that crowns a shot of espresso — and tried to combine them in a way that produced a well-rounded coffee facsimile, then added caffeine.
By contrast, traditional coffee alternatives like chicory and barley brews have nothing to offer a caffeine addict; Atomo, Minus, Northern Wonder, and Prefer are promising a reliable daily fix.
“Coffee is a ritual and it’s a result,” said Andy Kleitsch, the CEO of Atomo. “And that’s what we’re replicating.”
— L.V. Anderson
Read the full piece here to learn more about how researchers and entrepreneurs are thinking about the future of coffee.
More exposure
See for yourself
Last week, as we celebrated Looking Forward’s 100th issue, we launched a special opportunity that we are very excited about: a mini drabble writing contest.
Thank you to the many folks who have already submitted drabbles! We love reading all of your visions for a clean, green, just future. We’ve included the prompt here again, for those of you who are still percolating.
Also, we heard from a couple of y’all that the email address included in last week’s newsletter was bouncing. Thanks for letting us know — it should be fixed now!
***To submit: Send your drabble to lookingforward@grist.org with “Drabble contest” in the subject line, by the end of Friday, April 26.
Here’s the prompt: Choose ONE climate solution that excites you, and show us how you hope it will evolve over the next 100 years to contribute to building a clean, green, just future. We’ve covered a boatload of solutions you could draw from (100, in fact!) — so if you need some inspiration, peruse the Looking Forward archive here.
Drabbles offer a little glimpse of the future we dream about, so paint us a compelling picture of how you hope the world, and our lives on it, will evolve.
Here’s what we’re looking for:
- Descriptive writing that makes us feel immersed in the scene and setting.
- A sense of time. You don’t have to put a specific timestamp on your piece, but give us some clue that we are in the future (not an alternate reality), approximately 100 years from now, and that certain things have changed.
- A sense of feeling. Is this vignette about joy? Frustration? Excitement? Nervousness? The mundane pleasure of living in a world where needs are met? Make us feel something!
- 100 words on the dot.
The winning drabbles will be published in Looking Forward in May, and the winners will receive presents! Some Grist-y swag, and a book of your choice lovingly packaged and mailed to you by Claire.
A parting shot
Another climate-proof coffee company that Anderson covered is Stem; instead of cooking up a beanless imitation with more readily available ingredients, this company is working on growing coffee bean cells in a lab. Like cell-based meats, the product will have to clear regulatory hurdles before it can reach markets. But unlike root- and pit-based imitations, the resulting brew would be chemically identical to the real thing. These three photos show Stem’s coffee, from petri dish to pot.
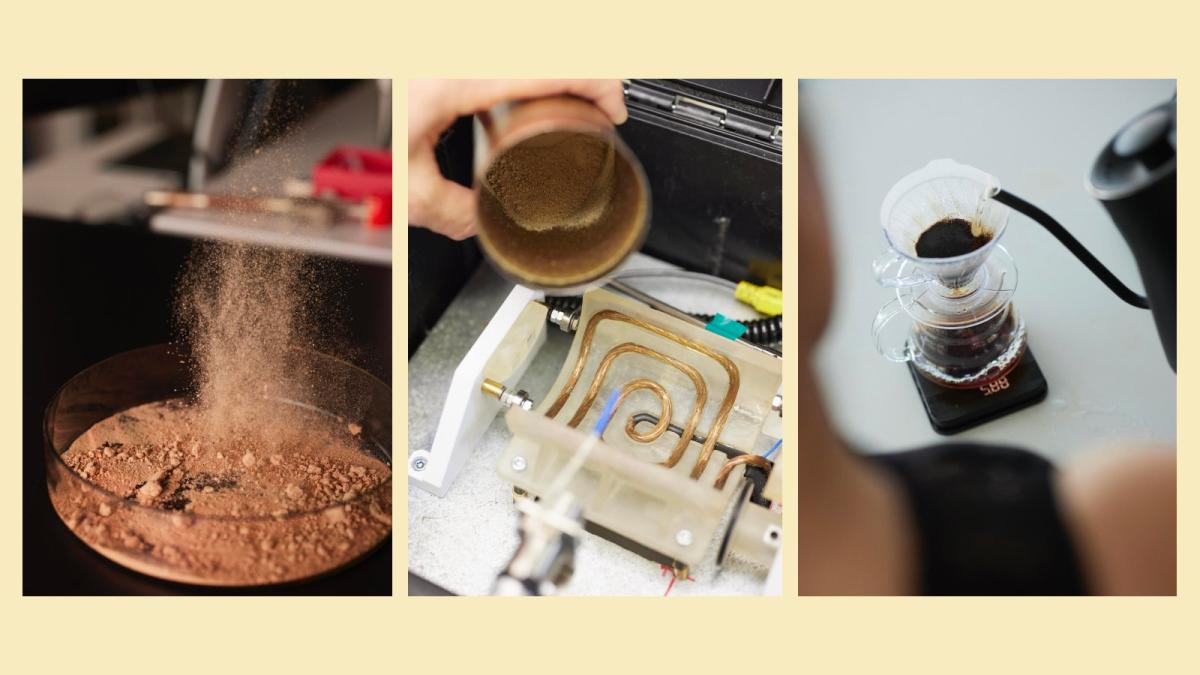
IMAGE CREDITS
Vision: Grist
Spotlight: L.V. Anderson / Grist; Jay Paull / Getty Images
Parting shot: Courtesy of Jaroslav Monchak / STEM
This story was originally published by Grist with the headline A wave of climate-conscious startups are brewing ‘beanless coffee’ on Apr 17, 2024.







